
Understanding how to index your website on Google is important. With an 89.99% market share (as of November 2025), Google still holds the largest search engine market share.
Getting your website indexed on Google (and ensuring it stays indexed) is crucial for increased online visibility. Google only displays web pages it indexes (stores in its digital library).
Unfortunately, research have shown that a large portion of websites aren’t indexed. Most websites that were indexed got deindexed. Google deindexes pages from time to time.
This shows why tools like IndexChecker.io are important to website owners. They let users check website indexing statuses and monitor webpages. That way, one can spot when issues arise and react timely.
Here, we discussed how you can get your website indexed on Google, and other helpful tips. Keep reading for more details.
What Is Google Index?
Before we divulge the steps you can take to get your website indexed on Google, let’s explain what Google indexing means.
Let’s say you have a computer and it has storage space (of course). You can store images, word documents, videos, and other files on that computer.
Google does something similar with the content you publish on your website. It keeps them in its digital library, and displays them when a user uses the right keyword.
So, what does Google indexing mean?
It refers to the list of websites (including web pages) Google has discovered and stores in its digital library. Once indexed, your website or web page will start to appear in Google’s search engine result page (SERP) for relevant queries.
What that means is, if the keyword of your indexed content is “Google index checker” and someone searches for similar content on Google. Your content could appear in the search result if Google deemed it to be better than others written on the same topic.
Getting Google to index your website is the first step. Once your pages are indexed, they become discoverable.
On the flip side, if your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t appear in the search result. It means Google doesn’t have them in its digital library.
Pro Tip: Stop assuming your content is discoverable after publishing on your website. You can use a URL inspection tool like IndexChecker.io to check your webpages to know if they have been indexed (and monitor them).
Aside from running Google index check on your website and pages, monitor them. Google can decide to de-index a web page for several reasons. It could technical or content-related.
The good thing is, you can fix the affected web pages and resubmit them to Google..
How To Get Google To Index Your Website Fast
How can you convince Google to index your website quickly? Follow the tips below:
1. Fix WordPress search engine visibility:
Is your WordPress website visible to search engines? Google can’t crawl or index your website if it’s not visible.
How can you make your website visible to search engines?
On WordPress, go to settings > Reading. Then scroll down to the “Search Engine Visibility” option.
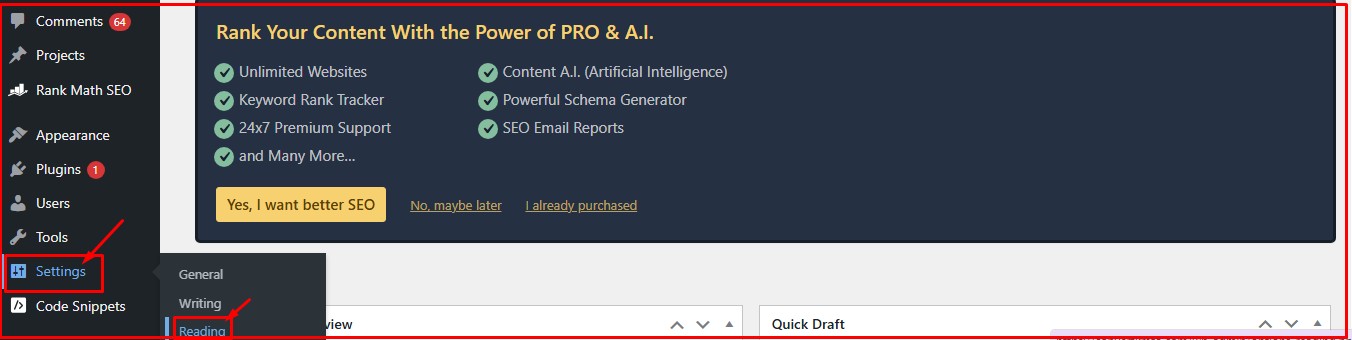
Save changes
Here’s what you need to know:
If you leave the check mark on, it means you don’t want search engines to crawl and index your website.
Remove the check mark if you want search engines to crawl and index your site.
After removing the check mark, click on “Save Changes” before leaving the page.
Now, you have authorized search engines to crawl and index your website from time to time.
2. Populate your website with valuable content:
Long form or publishing a large amount of content on your website won’t make Google indexing faster. Populating your website with low-quality, but well-optimized content won’t either.
Why? Google wants users to get value for their time.
Google wants people to find the right information and do so quickly. That’s why your well-optimized but low-quality content doesn’t get indexed. Why? You wrote for search engines, not for users.
Even if Google manages to index your low-quality posts, rest assured they would get deindexed in the future. Use URL inspection tools to check if some of your pages have already been deindexed.
Google’s latest Helpful Content Update algorithm shows the search engine’s preference for people-first, original and helpful content. Google is now using artificial intelligence and machine learning to fight unoriginal and low-quality content.
Key takeaways from Google’s recent algorithm update:
- Helpful content focus: Google values content created to help users to solve problems, and devalues those created to rank on search engines.
- Prioritize E-E-A-T: Google’s latest algorithm update reveals the high value the search engine giant now places on content that demonstrates experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness. Posts with unique insights and clear authorship are given high priorities.
- Relevance: Is your content relevant to your target audience, niche and target keyword? If your keyword is “how to index your website on Google Chrome” and you’re writing about the latest Google algorithm update, you’re misleading potential readers. Google hates such, and could penalize your site. Make your content relevant to the target audience and niche.
- User experience: While using clear bullet points and header structure improves user experience, Google’s latest updates also consider other factors. Other factors that influence a website’s UX include mobile-first design, core web vitals, and your pages’ interaction readiness.
- Search intent satisfaction: Your content should satisfy the search intent of users. In other words, it should answer all their questions completely.
The bottom line is to ensure your content is high-quality. That’s one of the ways to force Google to index your web pages faster.
How would you react if 60% of your computer’s storage is occupied by junks? What would you do? You probably would delete them to free up your computer’s storage space, right?
Google does something similar to low-quality content on its digital library. It deindexes them, so they don’t appear in the search engine result page.
So, if you want Google to index your website fast, and want your website to stay indexed, start posting high-quality, relevant and helpful content.
3. Sitemap creation and submission:
You can get Google to index your website faster by creating and submitting your sitemap?
But what is sitemap, and how can you create one? How can it influence your website’s indexing?
Below are the answer to the questions above.
Firstly, what is a sitemap? It’s a file that lists a site’s crucial pages, media, files, and other files.
Sitemap serves as a road map for search engines and users to understand a website’s structure and content. It improves a website’s discoverability and indexing.
Another thing you need to know about sitemap is that it can be in HTML format (for humans) or XML (for bots). It helps search engines understand which content is vital and when an update was initiated.
Having a sitemap will enable search engine crawlers to crawl a website more efficiently, particularly for new websites with poor internal linking or larger websites.
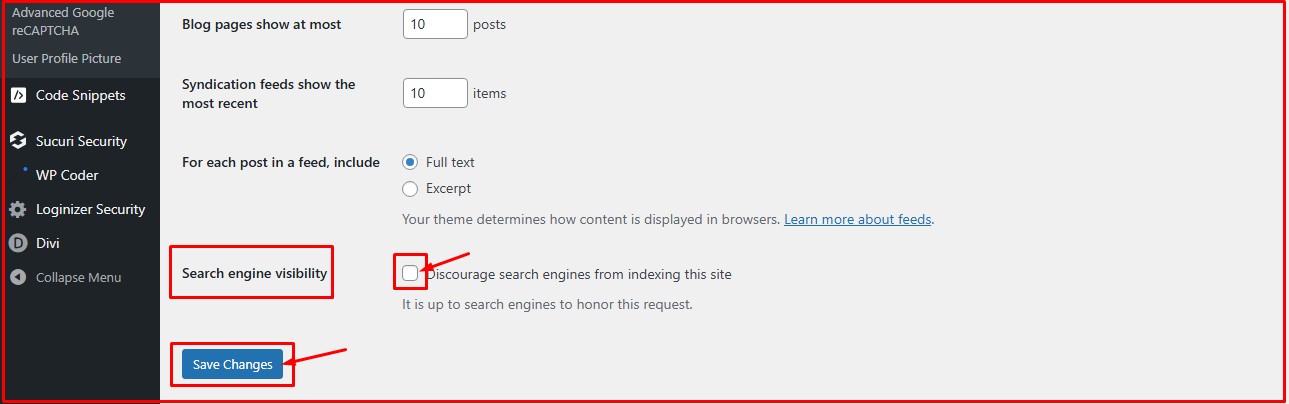
Here’s a sitemap of the website “convertkmto”
Add the “/sitemap.xml” to get the sitemap. We also discussed other ways you can get a website’s sitemap below.
You can get sitemap of a website via the following ways:
- Add (/sitemap.xml) to the website’s URL.
- Add (/sitemap) to the website’s URL
- Check the robots.txt file.
- Use an online sitemap generator
- Use Google search console for your own website.
Why is a sitemap so vital?
Creating a sitemap for your website offers several benefits.
- Improves indexing: Creating and submitting your sitemap will make it easier for search engines to identify and index your entire content.
- Better SEO: It benefits both large and new websites. It helps larger sites avoid missing pages, and makes new websites discoverable.
You can add your sitemap to Google via the Google Search Console (GSC). The search engine giant has already made provision to add sitemaps on GSC.
Adding your sitemap on the Google Search Console will enable Google to index your website faster. That way, your pages will start to appear in the search engine result pages.
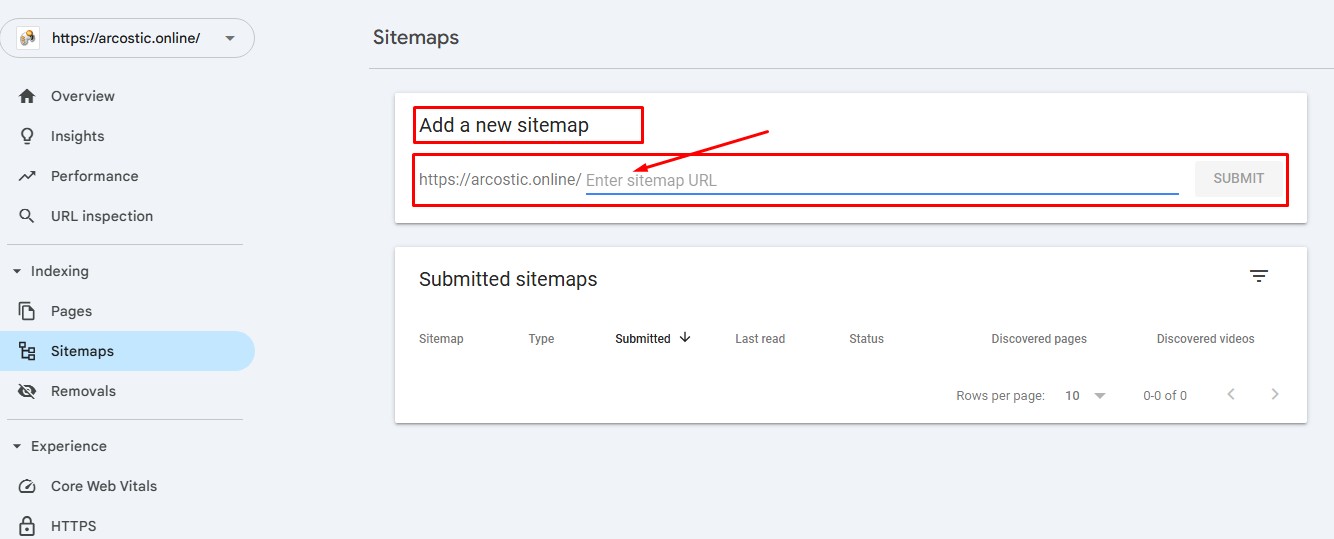
Enter your sitemap URL and click on “SUBMIT”. The process is that simple and quick.
4. Monitor your website’s indexing status:
Google staged the largest ever content removal (deindexing) in May 2025. Around 75% of indexed pages were deindexed.
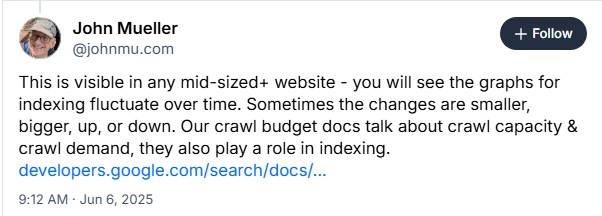
John Mueller, a webmaster trend analyst at Google also spoke about the indexing purge that took place in May 2025.
John’s comment on Bluesky (source) indicates that Google occasionally deindexes websites, even though he didnt state the reasons for Google’s indexing purge.
The indexing purge affected many top websites and brand. The reaction from the SEO community shows the purge affected websites of all shapes and sizes.
That’s why it’s important to monitor your website’s indexing status.
Don’t just publish content, create sitemaps, submit them and repeat the same routine over and over. Always keep an eye on your website’s indexing status.
How can you monitor your website’s indexing status?
While there are several tools out there, I am partial about indexchecker.io.
Using this tool, you can check your website’s indexing status, and equally monitor it. Through the detailed monitoring, you’ll know when issues arises, and take decisive steps to address them.
Here’s how to monitor your website’s indexing status.
Step #1: Visit indexchecker.io and create an account:
Click on “Get Started Here” to proceed. Then provide your email and choose a password for your account.
Step #2: Create an index monitoring project:
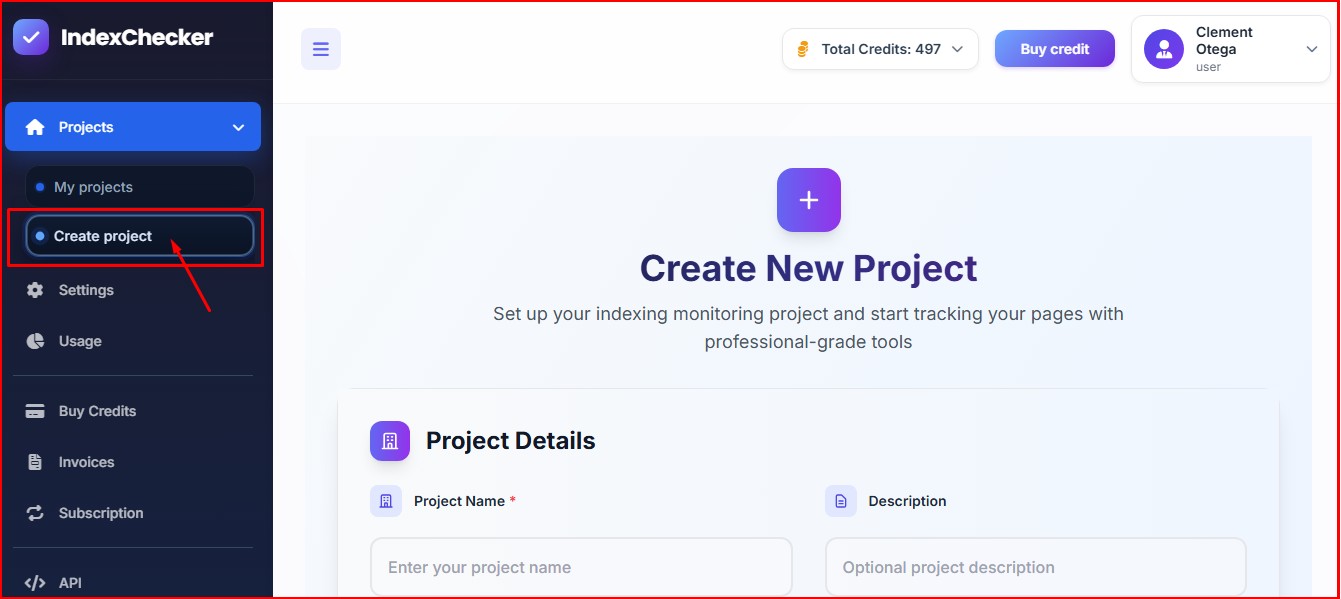
Click on “Create Project” to start your index monitoring project. The tool lets you track your web pages using profession-grade tools.
Add project name and description for proper organization of each project.
Step #3: Add your web pages:
Add the web pages you want to monitor. You can add as much as 2500 URLs on Indexchecker.io and monitor all of them simultaneously.
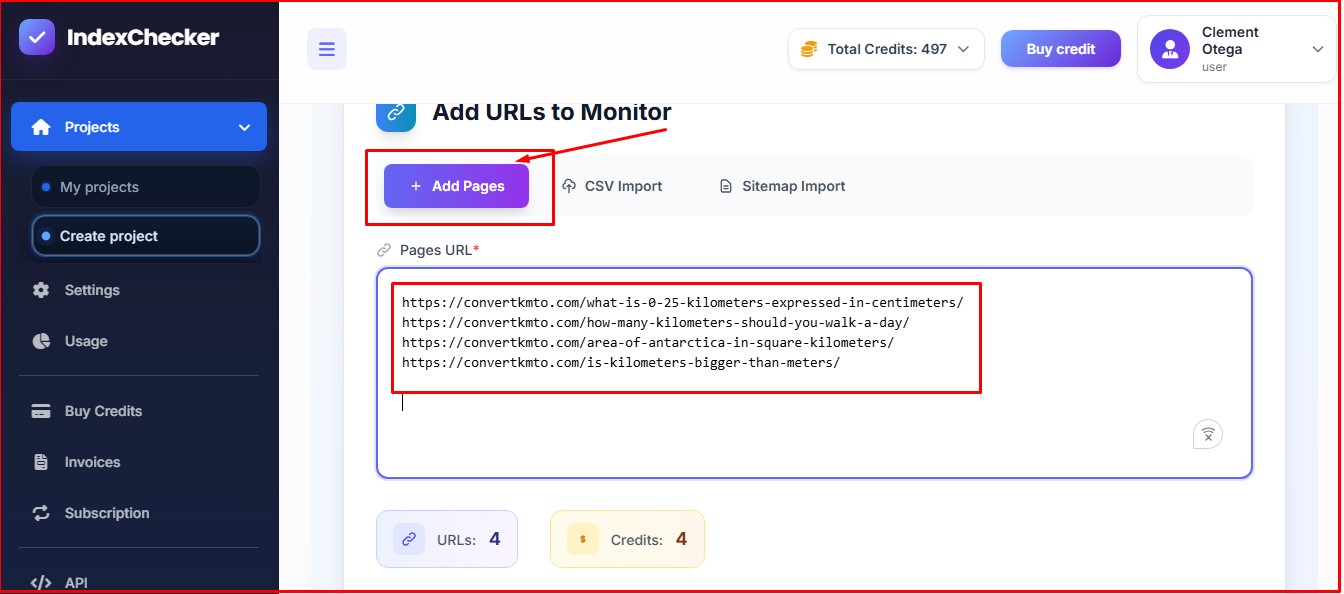
If you don’t want to add the URL of the web pages directly, you can import CSV or sitemap.
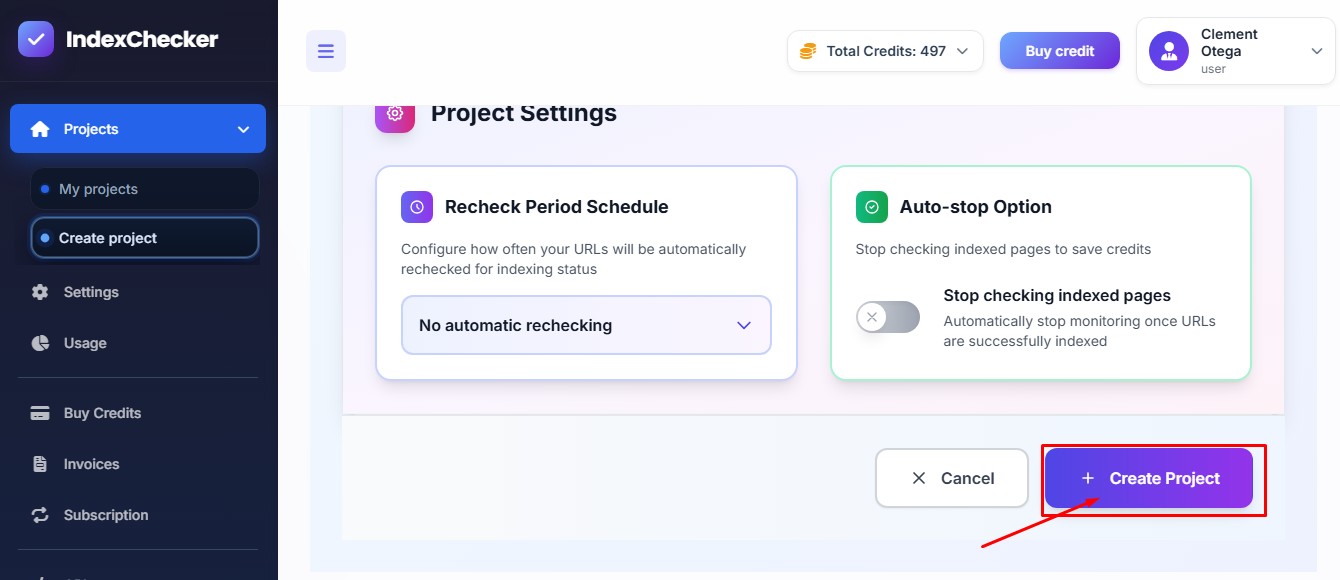
After adding the URLS, importing CSV or sitemap, click on “Create Project” to start analyzing the pages you want to monitor.
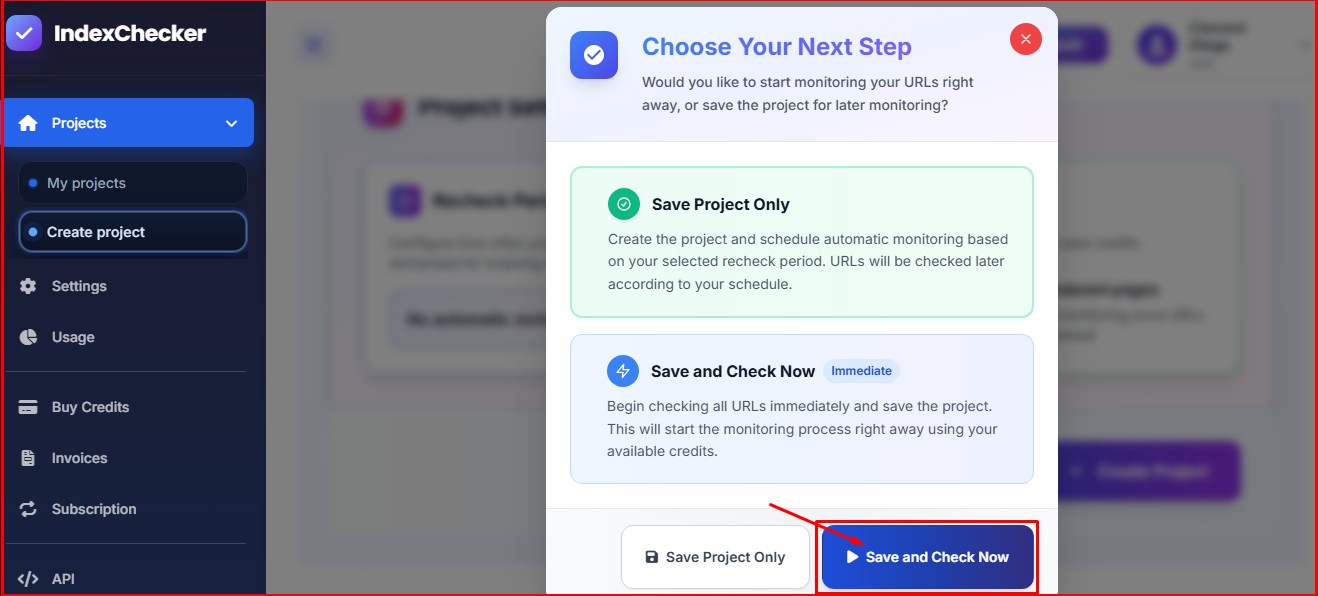
Click on “Save and Check Now” to check the indexing statuses of the pages, and start monitoring them automatically.
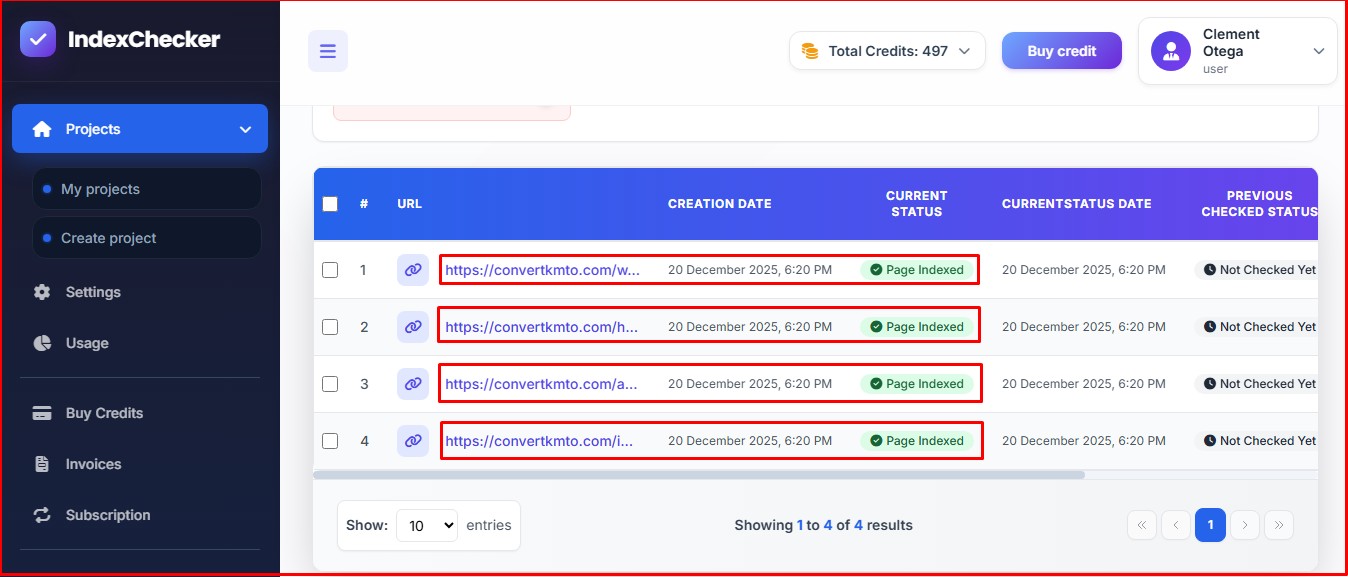
All four URLs checked. You can tell if the pages have been indexed or not from the dashboard. The tool also allows you to monitor each of the pages. That way, you’ll know when Google de-indexes any of the pages and respond quickly.
5. Fix internal links with no-follow tags:
Before Google indexes any webpage, it crawls it. That means, if Google is unable to crawl your webpage, it won’t index it.
One of the ways you can prevent Google from crawling your page is by using the nofollow tag.
If you have internal links with a rel= “nofollow” tag, then you’re telling Google not to crawl the content on that page.
Because the bots can’t crawl your page, no data will be sent to Google. Consequently, your page won’t appear on the search engine result page.
You can fix this problem by getting rid of the nofollow tags on the links. By so doing, Google bot will be able to follow the links and discover the linked pages.
6. Improve your backlink profile:
If you haven’t been taking backlink building seriously, now is the time to start doing so. Why? Backlinks are special. They have always been.
Backlinks are one of Google’s most important ranking factors, if not the most important. The search engine giant have held such views for backlinks for long, and it still does.
Why is backlink important?
Backlinks’ influence goes beyond improving a website’s search engine ranking. They can make Google index your website faster.
Backlinks from reputable websites indicate that your website and content are credible, valuable, and desires recognition. Google considers backlinks as vote of confidence.
That’s why it’s dangerous to obtain backlinks from spammy and low-quality websites. When you do, Google will view and rate your website the same way.
Pro Tip: Dofollow backlinks serve as great access point for Google to crawl and index a website. But when you’re acquiring backlinks, don’t focus only on getting the dofollow links.
Why you should not go for only dofollow links?
Google knows it’s practically impossible for all the websites you approach for backlink to permit dofollow tag. Most of them only allow the nofollow.
You can make your backlink profile natural by incorporating dofollow and nofollow links. Make it 60/40 percent dofollow to nofollow links.
Here’s how you can get quality backlinks:
- Publish backlink-worthy content: Ensure the articles you publish on your websites are high-quality, and unique. If that’s the case, you’ll get tons of backlinks from other websites without even requesting for them.
- Start guest posting: Approach reputable websites in your niche and offer to provide guest posts in specific topics. Ensure the topics are unique and haven’t been published on the sites. You can include a link to your website in the guest posts.
- Link insertion: You can approach website owners in your niche, particularly those you think one or more content on your website can serve as additional resource for their already published content.
- Find broken outgoing links: You can use tools like “Dead Link Checker” to search your competitors’ websites for broken links, and offer to replace them with a link from your website.
Ahrefs is another powerful and popular tool you can use to check a competitor’s website for broken links. Once you identify the broken links, offer to replace them with links from your site.
You can use the broken link building strategy to build more high-quality and valuable links that will have faster effect on our website’s ranking and indexing.
7. Fix your internal links:
Internal links doesn’t only help visitors discover more new pages, and navigate your website effortlessly. They help search engine discovers new pages on your website.
Proper internal linking can improve the rate at which Google will index your website. It also allows your new pages to get views, and spread page authority to other pages.
How do you create valuable internal links?
You can search your website for relevant pages getting higher organic traffic. Then link to new pages or pages getting low traffic. That’s a good way to create powerful internal links.
8. Fix duplicate pages issues on your website:
Having duplicate pages on your website? Fix them as quickly as possible. Duplication of pages could be a reason Google isn’t indexing your content.
If a page has content that’s 99% similar to another page (on the same website) or is duplicated, Google won’t index it. Google regard such as “unworthy content.”
How can you identify duplicate content on your website?
Sometimes, duplicate pages can be as a result of mistake. You may have forgotten that you had written content on a specific keyword. It can happen to anyone.
Here’s how you can identify and fix duplicate content. Below are tools you can use:
● Copyscape
● Siteliner

● Semrush
● Screaming Frog
● Google Search Console’s Index Coverage Report
You can use any of the above tools to search your website for duplicate content. Find and fix duplicate content preventing Google indexing.
9. Redirect or block low-quality webpages:
If you want to increase the number of times Google crawls and indexes your website, get rid of low-quality pages.
Understand this: Google has a limited amount of server resources. Therefore, if it crawl your website and find tons of low-quality pages, the number of times it crawls and indexes your website will reduce drastically.
It’s like visiting a friend who always keeps his house dirty. If you visit often and encounter the same thing, you may want to lower the number of times you stop by their house. Isn’t that so?
Google treats websites with tons of low-quality pages the same way. It will reduce the number of times crawls and indexes your website.
The solution is simple: Get rid of low-quality pages.
You can get rid of low-quality pages in two ways:
- Delete the low-quality pages from your website completely.
- Setup a 301 redirect for the low-quality pages. With this, you can point the low-quality pages to high-quality ones.
Pro Tip: Getting rid of low-quality pages from your website will improve its health, and increase its indexing time.
Conclusion
Now you know how to index your website on Google. But then, getting index shouldn’t be your primary concern. Staying indexed is. The most recent indexing purge shows that Google can deindex any website.
This makes monitoring your website’s indexing status more critical. That way, you can identify and react to issues faster.
With tools like indexchecker.io, you can check and monitor your website’s indexing status 24/7. You don’t need to spend hours monitoring your website’s indexing statuses manually any longer.
Google Indexing FAQ’s
What does Google Indexing means?
Google indexing or being indexed by Google means the search engine has discovered your web page or content, and added it to its database. By adding your web page to its database, your website will appear in the search engine result page when users search for related keyword. Your website won’t appear in the search engine result page (SERP) for relevant keyword if Google doesn’t index your web page or content.
Is it necessary to manually submit my website to Google for indexing?
You don’t necessarily have to submit your website to Google for it to index. However, doing so can speed up the process. You can help Google to discover your website quicker by submitting it on Google Search Console.
How long does Google indexing take?
The time it takes Google to index a website varies from one website to another. It depends on several factors like the websites quality, backlink quality, including how often the search engine crawls the website.
You can make Google index your website faster by publishing high-quality content, and building a healthy backlink profile. Acquire backlinks from niche-relevant and reputable websites.
Why has Google refused to index my website?
Google hasn’t refused to index your website because of your niche. The reason could be because of an existing problem on your website. The problem could be:
- Poor quality content
- Duplicate content
- No or poor quality backlinks
- No or poor internal linking structure
- Technical issues such as noindex tags
- Your website is new and hasn’t been discovered






