
Have you ever wondered why website owners ask questions like, “How long does it take for Google to index?” They have a good reason to ask, because the waiting period for Google to index a URL is one of the most tense. That’s because of the search engine’s unpredictability.
Google can crawl a page but not index it. It can also index the page without ranking it. Google can also deindex a page shortly after indexing it or after a long while.
The point is, people won’t find your content when they search on Google unless it’s indexed and ranked. Indexing means Google has identified your page’s URL, crawled, and indexed it (stored the content in its digital library).
Here, we discussed how long Google indexing takes and shared other tips to help you understand the process better. Keep reading for more details.
How Long Does Google Indexing Take?
According to Google’s John Mueller, indexing can take from a couple of hours to several weeks. We can also confirm this from experience.
Several factors influence Google indexing speed. Among them is the content quality, website and content’s age (new content on a new site might take longer to index), internal linking structure, crawl budget, website authority, XML sitemaps, and other technical SEO factors.
How To Determine If Google Has Indexed Your Page
The fact that you successfully published a piece of content on your website doesn’t mean Google will index it automatically.
While Google can index new and updated content on established websites faster (within a few hours to 3 days), it can take much longer to index new or updated content on a new website (less than 3 months old).
Here are the different ways you can check if Google has successfully indexed your page:
1. Use Google index checker:
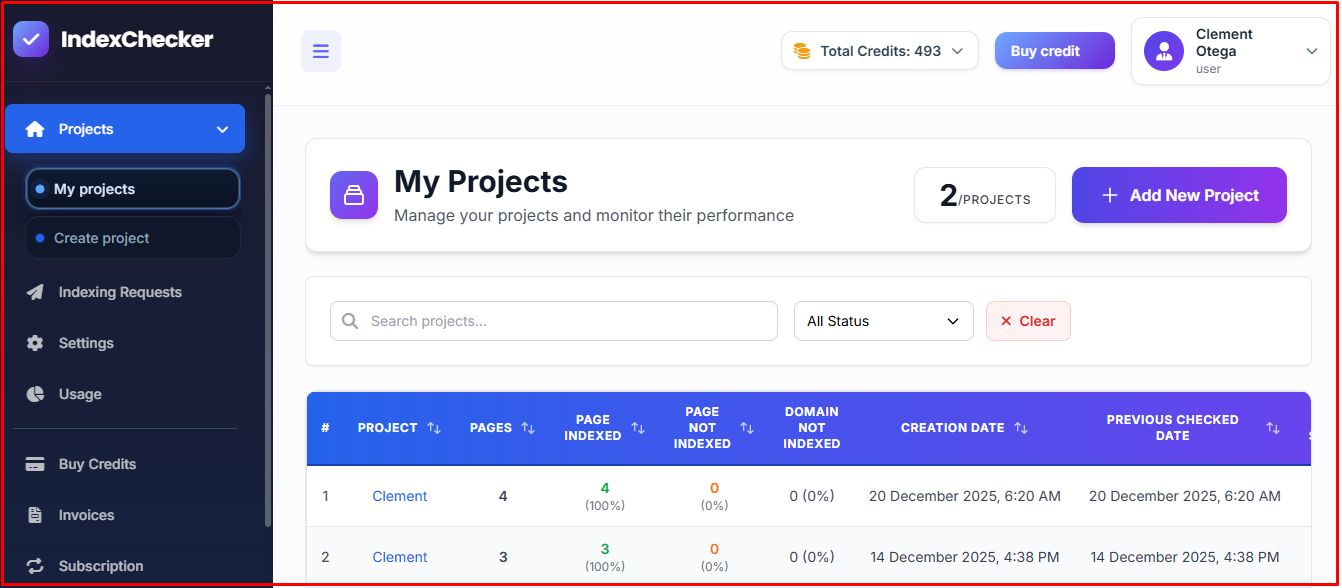
The majority of SEOs prefer using Google index checking tools. With these tools, they can check and monitor thousands of URLs from one dashboard.
Google index-checking tools like IndexChecker,io not only check and monitor thousands of URLs, but also provide detailed reports. Users receive notifications when the search engine de-indexes one or more URLs, so they can respond quickly.
2. Manual Google search:
You can find out if Google has indexed your website via a simple Google search. Enter site:yourdomain.com/page-url.
Here’s how to use it:
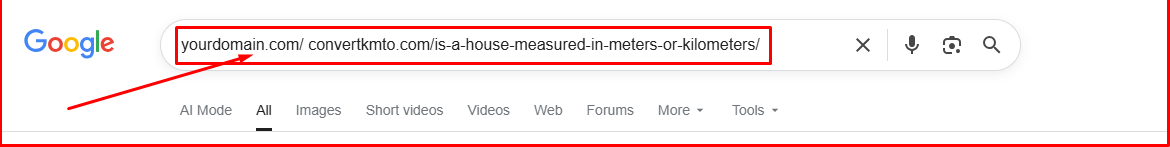
Site: convertkmto.com/is-a-house-measured-in-meters-or-kilometers/
Enter the above in the Google search bar. If the page appears in the Google search result, then it has been indexed by the search engine.
3. Google Search Console:
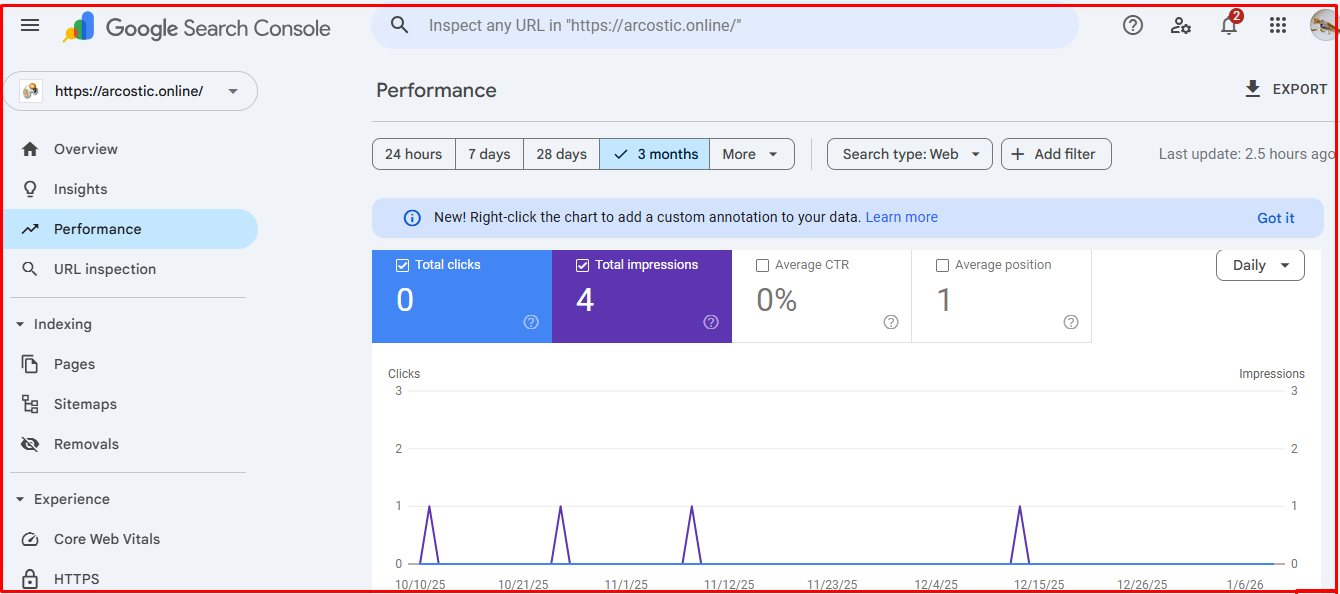
Here’s how you can use Google Search Console to check Google indexing of URLs.
- Login to your Google Search Console account
- Select the right property (website)
- Enter the URL you want to check. You’ll find a search bar located at the top of your dashboard.
- Review the report:
If you find a result that says “URL is on Google” it means the search engine has indexed the page. The fact that it has indexed the page is the reason why it appeared in the search engine result.
If you find another report that says “URL not on Google,” it means the search engine hasn’t indexed your page.
Google is kind enough to let website owners know the reason they didn’t index a URL. If it fails to index your URL, you’ll find the reason why. The reason could be “crawl errors” or “nonindex” tags.
Knowing the reason Google indexing failed will enable you to troubleshoot and resolve the issue quickly.
Pro Tip: If you check your Google indexing status and find a report like “discovered-currently not indexed” it means Google has identified your web page but hasn’t trusted it enough yet.
Why Google Doesn’t Index Most Pages
The dream of every website owner is not to build an aesthetically pleasing website. The primary goal is to get their web pages indexed and ensure they rank high in the search engine result page for relevant keywords.
Google would love to index almost every web page it crawls. But it’s so unfortunate that it can’t happen. Most reasons Google doesn’t index a web page is the website owner’s fault.
So, if Google doesn’t index your web page, the below reasons could be responsible:
- Shallow content depth: A piece of content with poor depth may struggle to get indexed by Google. In other words, poor content depth can make Google to refuse to indexing a web page.
- Weak domain trust: This usually happens to new websites (less than 3 months old) and the ones that haven’t built real authority. Google might delay or refuse to index a page from a website with a weak
- Duplicate content: Allowing different versions of your website’s URL to exist can cause duplicate content issues. Unless you choose a primary canonical URL version, Google will treat the other URL versions as separate entities.
Duplicate content can split link equity, and make indexing difficult. It’s an annoying way to waste the crawl budget.
Impact of Content Length on Indexing Speed
Google has stated times without number that it places higher value on content quality than length. Indexing of 3000-word content with no real substance can take longer time than a 2000-word in-depth and high-quality content. In most cases, Google might index the former.
Content length becomes important when the content in question is high-quality. Therefore, bear in mind that length alone cannot influence indexing speed. You need your content to have proper depth.
Google will ensure your page gets indexed faster when your content:
- Shows that you possess subject-matter expertise on the topic.
- Satisfies the search intent of users fully
- Naturally addresses related subtopics
Google wants your content to be different from the ones already indexed. It doesn’t make sense indexing a piece of content that’s similar to what the search engine has already stored in its digital library.
When you write a piece of content that stands out, Google will index it without thinking twice.
Impact of Backlinks on Indexing Speed
Backlinks are important ranking factors. In fact, they are one of the most, if not the most important Google ranking factors.
Does backlink increase indexing speed? It does indirectly.
Here’s how backlinks can help your page get indexed much faster:
- Improvement in trust signals
- Improvement in crawl priority
- Accelerate page’s discovery
A single backlink from a high authority website can make indexing speed faster than manual URL submission. That’s how important backlinks are.
Building a healthy backlink profile will increase your page’s ranking and authority, making it discoverable and highly valuable in Google’s views.
Mobile-friendliness and Impact on Google Indexing
Having a mobile-friendly website isn’t a thing of choice, but a necessity. With over 5.8 billion people (more than 70% of the world population) using mobile phones, building a mobile-friendly website has never been more important.
Research shows that 64.35% of global web traffic comes from mobile devices. You increase organic traffic by making your website mobile-friendly.
How does mobile-friendliness improve Google indexing speed?
Google has stated clearly that it indexes the mobile-version of a website before other versions.
Indexing increases if your website:
- Loads fast
- Has no broken layout
- A breeze to navigate and doesn’t hide content.
Pro Tips: Google can de-prioritize, delay or even abandon your website’s indexing if the desktop version of the website is perfect while the mobile-version isn’t.
Conclusion
So, how long does it take for Google to index? It can take a few hours to weeks. Several factors determine how long Google indexing might take. New content published on a brand new website might take a bit longer. Low-quality content that lacks depth might take longer or even end up not getting indexed.
We discussed the different strategies you can implement to improve indexing speed. For instance, a mobile-friendly website has a better chance of faster Google indexing than one that’s more perfect on desktop. Google indexes the mobile version of every website before considering the other versions.
Google Indexing FAQ’s
Can Google index a web page in a few minutes?
Yes, Google has the capacity to index a page within a few minutes. But that would depend on the website’s authority and crawl budget. Google discovers and indexes pages of high-authority websites with a strong crawl budget faster.
Why does Google crawl but not index my page?
Several factors could be responsible. These include low-content value, weak authority, duplicate content or other technical SEO issues discouraging the search engine from indexing the page.
What number of times should I request reindexing?
Request for reindexing the first time, and again if the first wasn’t accepted. However, don’t request for reindexing unless you have made significant improvement on the content. Google will ignore your content if you keep submitting without meaningful improvement.
Does URL submission guarantee Google indexing?
URL submission will request crawling. Google decides if the page should be indexed or not after crawling it. Google can crawl a page and not index it. It can also index a page and later de-index it.
How do I know if Google has deindexed my page?
There are several ways you can find out. You can check manually or get an automatic report when Google deindexes your page. Tools like IndexChecker.io allow you to automate URL monitoring.






